An Introduction to Stiff ODEs with Python
Notice: In my previous post on stiff ODEs, I demonstrated how different ODE solvers in Matlab perform with a few examples. The live script for the post is also provided for educational purpose. In this post, I will do the same in Python. You can find the ipynb file in the same repository.
Info: The solver interfaces provided by Matlab and SciPy are not exactly the same (SciPy uses rtol*abs(y)+atol while Matlab uses max(rtol*abs(y),atol)), so we will use different solvers and tolerances. . If you are interested, please refered to the SciPy document and the Matlab document.
It’s well-known that stiff ODEs are hard to solve. Many books are written on this topic, and SciPy even provides solvers specialized for stiff ODEs. It is easy to find resources, including the wikipedia entry, with technical and detailed explanations. For example, one of the common descriptions for stiff ODEs may read:
An ODE is stiff if absolute stability requirement is much more restrictive than accuracy requirement, and we need to be careful when we choose our ODE solver.
However, it’s fairly abstract and hard to understand for people new to scientific computing. In this post, I hope to make the concept of stiffness in ODEs easier to understand by showing a few examples. Let’s start with a simple (non-stiff) example, and compare it with some stiff examples later on.
Example 1
Let’s consider a non-stiff ODE
\[y'=Ay\]where \(A=\lambda\)
In the first case we have \(\lambda=-0.1\). The solution is
\(y(t)=e^{-0.1t}y(0)\),
meaning we have a exponential decaying function.
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp, RK45
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mlambda = -1e-1
A = np.matrix([mlambda])
F = lambda t,u: A.dot(u.flatten())
# initial condition
u0 = np.ones(A.shape[0])
# time points
t = [0,10]
RK45
We can look at the solution from RK45:
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'RK45',rtol=1e-7,atol=1e-7)
# # # # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0], 'o-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
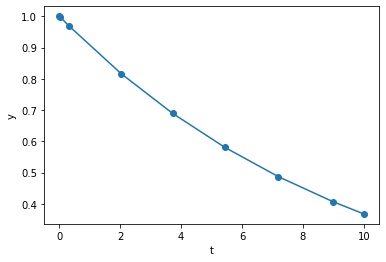
As we can see, it RK45 gives us a decaying function. In this interval, RK45 used
sol.t.size
9
steps to achieve the specified tolerance.
Example 2
Let’s consider the same equation
\[y'=Ay\]but now \(A=\begin{bmatrix}\lambda_1 & \\ & \lambda_2\end{bmatrix}\)
In the first case we have \(\lambda_1=-0.1,\ \lambda_2=10^3\lambda_1\). This means we have two decoupled equations. The solution is
\(y(t)=\begin{bmatrix}y_1(t)\\y_2(t)\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}e^{-0.1t}y_1(0)\\e^{-100t}y_2(0)\end{bmatrix}\), meaning we have two exponential decaying functions.
mlambda1 = -1e-1
mlambda2 = 1e3*mlambda1
A = np.diag([mlambda1, mlambda2])
F = lambda t,u: A.dot(u)
# initial condition
u0 = np.ones(A.shape[0])
# time points
t = [0,10]
RK45
We can use RK45 to solve it in the same fashion:
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'RK45',rtol=1e-7,atol=1e-7)
# # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[1],'o-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
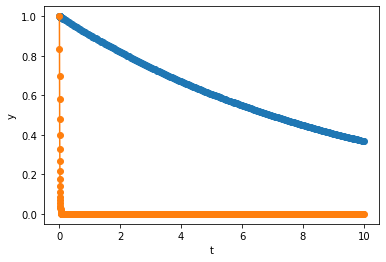
This time we get 2 decaying functions, and \(y_2\) decays much faster then \(y_1\). In this same interval, RK45 used
sol.t.size
333
steps to achieve the desired error tolerance. In this example, \(y_1\) is exactly the same as the solution in Example 1, but it take much longer to calculate. One may think the step size of RK45 is limited by the accuracy requirement due to the addition of \(y_2\). However, this is clearly not the case since \(y_2\) is almost identically \(0\) on the entire interval. What is happening here is that, the step size of RK45 is limited by the stability requirement of \(y_2\), and we call the ODE in Example 2 stiff.
SciPy provides specialized ODE solvers for stiff ODEs. Let’s look at BDF and Radau
BDF
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'BDF',rtol=1e-7,atol=1e-7)
# # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[1],'o-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
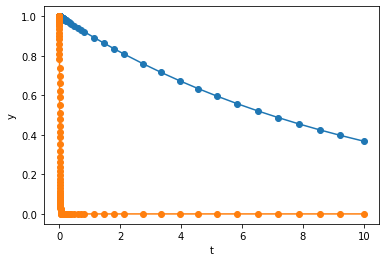
BDF takes
sol.t.size
134
Radau
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'Radau',rtol=1e-7,atol=1e-7)
# # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[1],'o-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
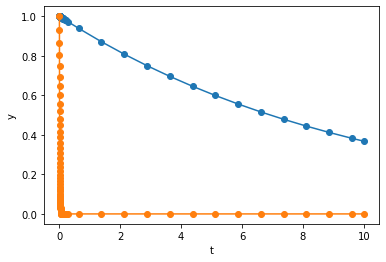
and Radau takes
sol.t.size
85
steps. Apparently, BDF and Radau is significantly more efficient than RK45 for this example. From the figure above, we can also see that BDF and Radau stratigically used shorter step size when \(y_2\) is decaying fast, and larger step size when \(y_2\) flattens out.
At this point you may think that if you don’t know whether an ODE is stiff or not, it is always better to use BDF and Radau. However, this is not the case, as we will show in the next example.
Ocsillatory ODE
Example 3
Let’s look at an oscillatory ODE
\[y'=Ly\]and \(L=\begin{bmatrix} & \lambda\\-\lambda & \end{bmatrix},\ \lambda=-0.1\)
The eigenpairs of \(L\) are
\[(\pm\lambda i,\;\begin{bmatrix}1 \\ \pm i\end{bmatrix})\]The solution is oscillatory because the eigenvalues are imaginary.
mlambda = -1e-1
L = np.matrix([[ 0, mlambda],[ -mlambda, 0]])
F = lambda t,u: L.dot(u.flatten())
# initial condition
u0 = np.ones(L.shape[0])
# time points
t = [0,50]
RK45
Let’s look at the solution from RK45
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'RK45',rtol=1e-7,atol=1e-7)
# # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[1],'o-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
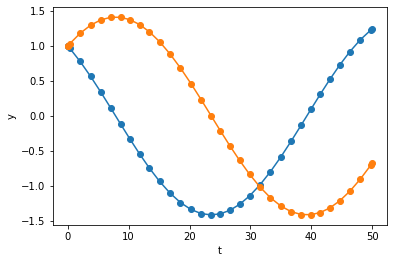
sol.t.size
34
As expected, we see two slow oscillatory functions.
Example 4
Now let’s look at a stiff oscillatory ODE
\[y'=Ly\]and \(L=\begin{bmatrix}& A\\ -A &\end{bmatrix},\: A=\begin{bmatrix}\lambda_1 & \\ & \lambda_2\end{bmatrix}\)
The eigenpairs of \(L\) are \(\begin{pmatrix}\pm \lambda_1i, \begin{bmatrix}1 \\ 0 \\ \pm i \\ 0\end{bmatrix}\end{pmatrix}\) and \(\begin{pmatrix}\pm \lambda_2i, \begin{bmatrix}0 \\ 1 \\ 0 \\ \pm i\end{bmatrix}\end{pmatrix}\)
Similar to before, we set \(\lambda_1=0.1, \lambda_2=100\lambda_1\). Now we have both fast and slow oscillatory functions in our solution.
mlambda1 = -1e-1
mlambda2 = 1e2*mlambda1
A = np.diag([mlambda1, mlambda2])
L = np.block([[np.zeros([2,2]),A],[-A,np.zeros([2,2])]])
F = lambda t,u: L.dot(u.flatten())
# initial condition
u0 = np.ones(L.shape[0])
# time points
t = [0,50]
RK45
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'RK45',rtol = 1e-6, atol = 1e-6)
# # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[1],'-',sol.t,sol.y[2],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[3],'-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
Text(0, 0.5, 'y')
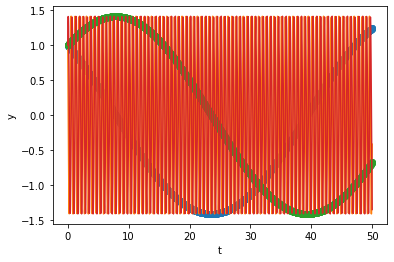
In the plots we can see both slow and highly oscillatory parts. Again, similar to the decaying case, now RK45 is taking shorter step sizes because of the the fast oscillating part, even though and could have taken much shorter time steps like the example above. In this case,
sol.t.size
1772
This time BDF and Radau are not that efficient either.
BDF
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'BDF',rtol = 1e-6, atol = 1e-6)
# # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[1],'-',sol.t,sol.y[2],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[3],'-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
Text(0, 0.5, 'y')
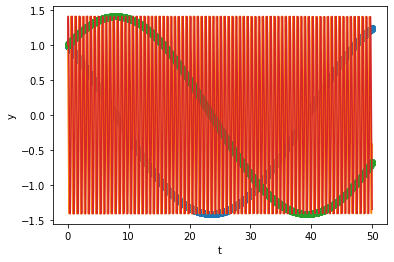
sol.t.size
3853
Radau
# solve ODE
sol = solve_ivp(F,t,u0,'Radau',rtol = 1e-6, atol = 1e-6)
# # plot results
plt.plot(sol.t,sol.y[0],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[1],'-',sol.t,sol.y[2],'o-',sol.t,sol.y[3],'-')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
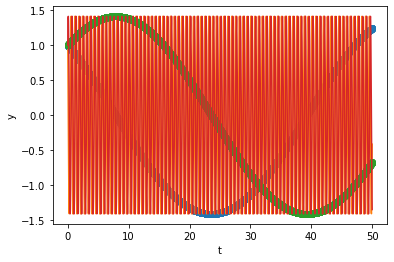
sol.t.size
3788
Notice highly oscillatory and stiff ODEs are generally hard to solve. All the solvers, RK45, BDF, and Radau take very short steps and become very expensive.
Info: You may feel the examples here are quite artificial since they are all linear and the analytical solutions are available. However, I feel it’s pedagogical to introduce stiffness in a simple setting like this. There will be a future post demonstrating stiff ODEs in nonlinear cases.
This blog post is published at https://edwinchenyj.github.io. The pdf version and the source code are available at https://github.com/edwinchenyj/scientific-computing-notes.
Leave a comment